Ligament & Muscular Injuries
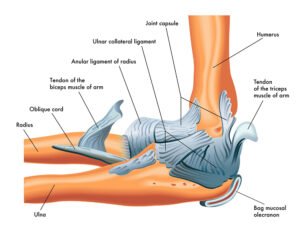
Ligament and muscular injuries are common types of musculoskeletal injuries that can occur due to trauma, overuse, or improper movement. Here’s an overview of their aspects:
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect bones to each other, providing stability to joints, while muscles are contractile tissues responsible for movement. Injuries to ligaments and muscles can range from mild strains and sprains to severe tears and ruptures, leading to pain, swelling, and functional impairment.
Preventing ligament and muscular injuries involves proper conditioning, warm-up, and technique, as well as using appropriate protective equipment and following safety guidelines during physical activity. Seeking prompt medical attention for ligament and muscular injuries can help prevent complications and facilitate a faster recovery, allowing individuals to return to their activities with reduced risk of reinjury.
Symptoms of ligament and muscular injuries may include:
Pain: Acute or chronic pain at the site of the injury, often worsened by movement or weight-bearing activities.
Swelling: Swelling, inflammation, or bruising around the affected area, indicating tissue damage or inflammation.
Instability: Feeling of joint instability or “giving way” of the affected limb, particularly with weight-bearing activities.
Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the injured joint or limb, stiffness, or loss of flexibility.
Muscle Weakness: Weakness or loss of strength in the affected muscle or muscle group, making it difficult to perform certain movements or activities.
Ligament and muscular injuries can be caused by various factors, including:
Trauma: Direct trauma, such as falls, collisions, or sudden impacts, can cause ligament sprains, muscle strains, or tears.
Overuse: Repetitive stress or overuse of muscles and ligaments, particularly without adequate rest or recovery, can lead to microtrauma and tissue damage.
Poor Conditioning: Inadequate warm-up, cool-down, or conditioning exercises can increase the risk of muscle and ligament injuries during physical activity.
Improper Technique: Incorrect form or technique during sports, exercise, or daily activities can place excessive strain on muscles and ligaments, leading to injury.
Biomechanical Factors: Structural abnormalities, muscle imbalances, or poor posture can predispose individuals to ligament and muscular injuries.
Treatment options for ligament and muscular injuries depend on the type, severity, and location of the injury but may include:
Rest and Immobilization: Resting the injured area and immobilizing it with a brace, splint, or cast to promote healing and prevent further damage.
Ice and Compression: Applying ice packs and compression bandages to reduce swelling, inflammation, and pain.
Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises, stretching, and strengthening programs to restore mobility, strength, and function.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications to alleviate pain and discomfort.
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair torn ligaments or muscles, particularly if conservative treatments fail to provide relief.

